SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) is domain-specific programming language for working with relational databases. A database is any organized collection of data; a relational database is one where the data inside adheres to certain mathematical "relations" which permit the operations of "relational algebra." The underlying math is unimportant for our needs, but you should be aware of the following points:
- Relational databases are just one of the many possible choices for database structure. Relational databases are old and well-established, but other types (e.g. document databases) have been growing in popularity. In particular, time-series databases like InfluxDB could be a reasonable choice for our telemetry system.
- Even with the relational database category, there are multiple engines to choose from, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, SQLite, etc.
- Almost all types of databases operate around the idea of a "table". Tables are where you actually store the data in the database; each table associates its columns with the data in its rows.
- SQL is a language for managing relational databases. It is not a general purpose programming language like Python—it is not meant to be used for arbitrary computations. And although there are many advanced features of SQL that database engineers leverage, we only ever use a very small subset of SQL in our system.
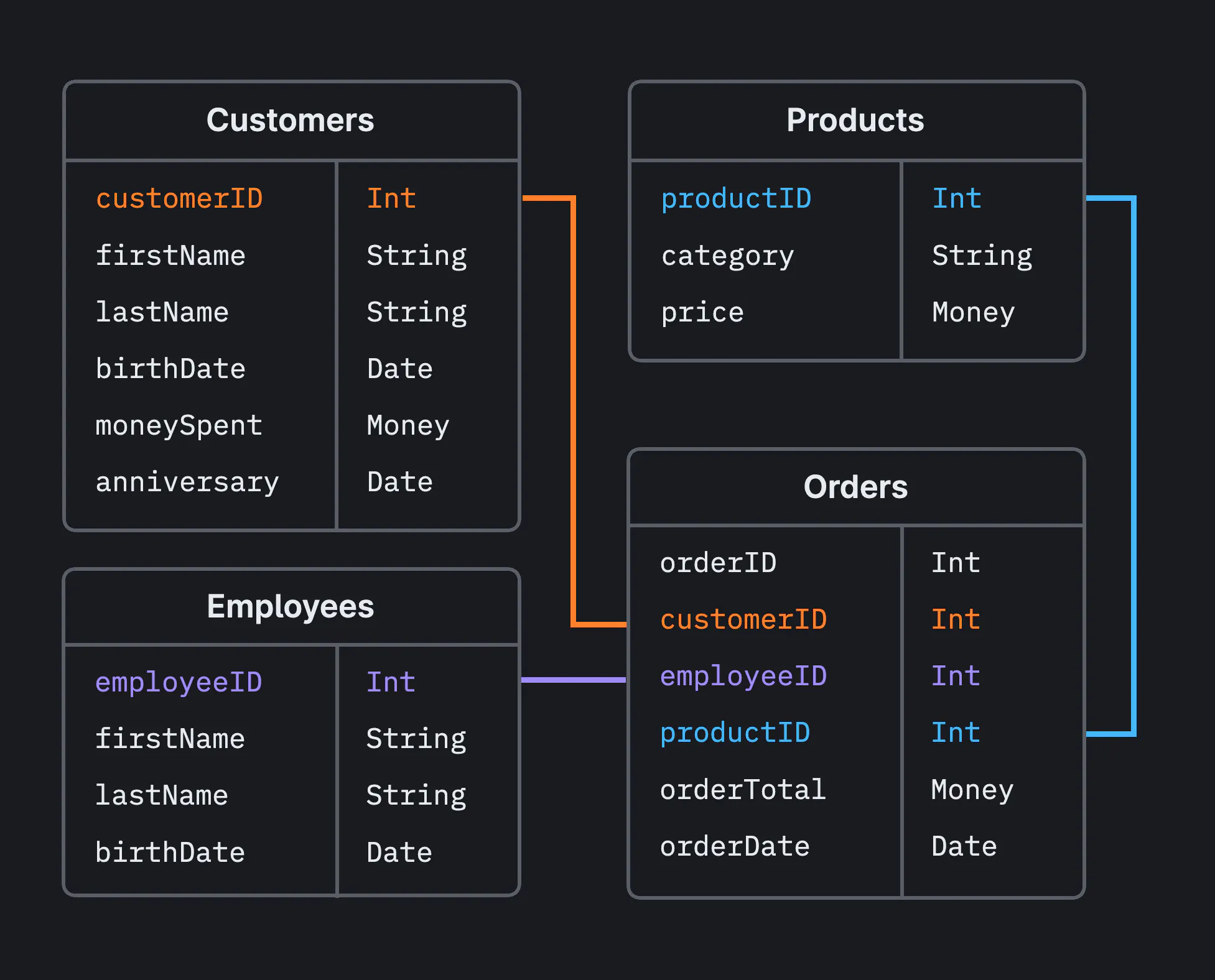 Example schema for a relational database
Example schema for a relational database